

#Velocity vs time graph how to
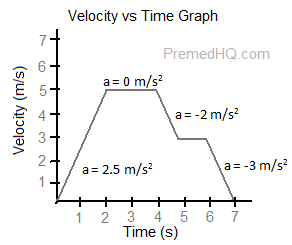
time graph.Įxample (1): In this example, we want to know how to read a position-time graph. Next, subtract the initial position from the final one to get the displacement vector using a position vs. To find the displacement of a moving object on a position-time graph, first, locate two points on the graph, and specify them as initial and final points at that time interval, then find their corresponding positions from the vertical axis. Remember that the difference of initial and final positions of a moving object is defined as displacement in physics, or precisely in math is written as below, \ where $x_f$ is the final position, and $x_i$ is the initial position of the object. In such graphs, the first quantity, position, is placed on the vertical axis and the other quantity, here time, is on the horizontal axis. time graphĪs its name indicates, the position-time graph shows the position of a moving object relative to the starting point at each instant of time. How to find displacement on a position vs. In this article, we want to answer these questions with plenty of worked examplesįirst of all, we study the displacement vector which is the core concept in studying kinematics. The area below the time axis would be negative as v is negative.

(ii) the area between the curve and below the time axis. (i) the area between the curve and above the time axis and. In addition, using a position-time graph, one can find displacement, average speed and velocity, and acceleration of motion. Explanation: Area below the curve is distance in a velocity time graph gives the distance, However, to find the displacement we need to break the area into two parts. time graph aims to analyze and identify the type of motion. Time Graph: Worked Examples for High Schools


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
